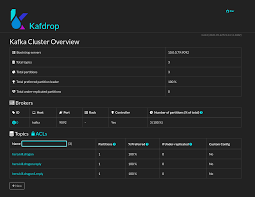
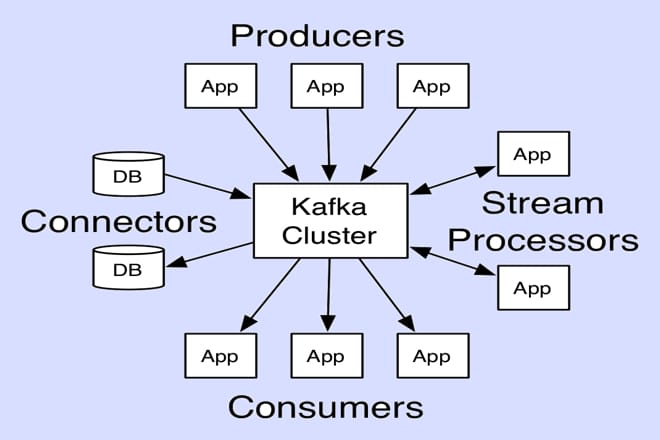
Kafdrop is a powerful, open-source web-based UI for monitoring and managing Apache Kafka clusters. It provides a user-friendly interface to view topics, partitions, consumer groups, and messages, making it an essential tool for developers and administrators working with Kafka. Whether you’re troubleshooting data pipelines or analyzing message flow, Kafdrop simplifies the process with its intuitive design and robust features, enabling seamless interaction with Kafka’s complex ecosystem.
Installing Kafdrop requires a clear understanding of your environment, including prerequisites like Java, Docker, or direct binary setups. This guide walks you through the installation process step-by-step, ensuring you can deploy Kafdrop efficiently. From setting up dependencies to configuring Kafdrop for your Kafka cluster, we cover every aspect to help you avoid common pitfalls and streamline your workflow.
By following this comprehensive tutorial, you’ll learn multiple methods to install Kafdrop, including Docker, JAR files, and source code compilation. Each approach is tailored to different use cases, whether you’re running a local development setup or a production-grade cluster. Let’s dive into the installation process, explore configuration options, and ensure your Kafdrop instance is up and running smoothly.Kafdrop and Its Dependencies
What Is Kafdrop?
Kafdrop is a lightweight, web-based tool designed to manage and monitor Apache Kafka clusters. It offers a visual interface to browse topics, inspect messages, and track consumer group offsets. Built in Java, Kafdrop is compatible with most Kafka versions, making it versatile for various environments. Its open-source nature allows customization, ensuring it fits specific project needs. Understanding its core functionality helps you choose the right installation method.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before installing Kafdrop, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. You need a running Kafka cluster with ZooKeeper or KRaft for configuration management. Java (version 11 or higher) is essential for running Kafdrop’s JAR file, while Docker simplifies containerized deployments. A stable internet connection is required for downloading dependencies. Verifying these components ensures a smooth installation process without unexpected errors.
Compatibility with Kafka Versions
Kafdrop supports Apache Kafka versions 0.10.0 and above, ensuring broad compatibility. It integrates seamlessly with both older and newer Kafka setups, including those using KRaft for Raft-based consensus. Always check your Kafka version before installation to avoid mismatches. Kafdrop’s documentation provides detailed compatibility notes, helping you align the tool with your cluster’s configuration. This ensures optimal performance and functionality.
Installing Kafdrop Using Docker
Setting Up Docker Environment
Docker provides a quick and efficient way to deploy Kafdrop. First, ensure Docker is installed on your system by running docker –version. Download the Kafdrop Docker image from Docker Hub, which contains pre-configured dependencies. Set up a Docker network to connect Kafdrop with your Kafka cluster. This approach minimizes manual configuration and ensures a clean, isolated environment.
Running Kafdrop Docker Container
To run Kafdrop via Docker, use the following command:
- docker run -d –name kafdrop -p 9000:9000 obsidiandynamics/kafdrop –kafka.brokerConnect=<broker>:9092
- Replace <broker> with your Kafka broker’s address.
- The -p 9000:9000 flag maps port 9000 to access Kafdrop’s UI.
- Add –zookeeper.connect=<zookeeper>:2181 if using ZooKeeper. This command launches Kafdrop, accessible at http://localhost:9000.
Configuring Docker for Production
For production environments, configure Docker with persistent storage to retain Kafdrop settings. Use a docker-compose.yml file to define services, including Kafdrop, Kafka, and ZooKeeper. Set environment variables for secure connections, such as SSL or SASL. Ensure resource limits (CPU, memory) are defined to prevent performance issues. Regularly update the Kafdrop image to leverage the latest features and security patches.
Installing Kafdrop Using JAR File
Downloading the Kafdrop JAR
The Kafdrop JAR file is available on GitHub or Maven Central. Visit the official Kafdrop repository to find the latest release. Download the JAR file (e.g., kafdrop-<version>.jar) to your server or local machine. Ensure you select a version compatible with your Kafka cluster. This method suits environments where Docker isn’t preferred or available.
Setting Up Java Environment
Kafdrop requires Java 11 or higher to run the JAR file. Verify your Java version with java -version. If outdated, install a compatible JDK from Oracle or OpenJDK. Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to point to your JDK installation. Ensure your system has sufficient memory, as Kafdrop may consume significant resources during heavy monitoring tasks. This setup ensures smooth execution.
Running Kafdrop with JAR
To start Kafdrop, run the command: java -jar kafdrop-<version>.jar –kafka.brokerConnect=<broker>:9092. Replace <broker> with your Kafka broker’s address. Optionally, specify ZooKeeper with –zookeeper.connect=<zookeeper>:2181. Access the UI at http://localhost:9000. For production, configure JVM options like -Xms and -Xmx to optimize memory usage. Monitor logs for errors during startup to troubleshoot issues.
Building Kafdrop from Source
Cloning the Kafdrop Repository
For advanced users, building Kafdrop from source offers customization. Clone the Kafdrop GitHub repository using git clone https://github.com/obsidiandynamics/kafdrop.git. Ensure Git is installed on your system. Navigate to the cloned directory with cd kafdrop. This method allows you to modify the source code, add features, or integrate with specific Kafka configurations before building.
Installing Build Tools
Building Kafdrop requires Maven and Java 11 or higher. Install Maven with mvn -version to verify. If missing, download it from the Apache Maven website. Ensure your JAVA_HOME variable points to a compatible JDK. Maven manages dependencies, such as Spring Boot and Kafka libraries, automatically. A stable internet connection is necessary to download these dependencies during the build process.
Compiling and Running Kafdrop
Run mvn clean package in the Kafdrop directory to compile the source code. This generates a JAR file in the target directory. Execute the JAR with java -jar target/kafdrop-<version>.jar –kafka.brokerConnect=<broker>:9092. Access the UI at http://localhost:9000. Customize the build by editing the pom.xml file for specific dependencies. Test the build locally before deploying to production.
Configuring Kafdrop for Your Kafka Cluster
Connecting to Kafka Brokers
To connect Kafdrop to your Kafka cluster, specify the broker address in the configuration:
- Use –kafka.brokerConnect=<broker>:9092 for Docker or JAR setups.
- Multiple brokers can be listed as a comma-separated string (e.g., broker1:9092,broker2:9092).
- Ensure brokers are accessible from Kafdrop’s host.
- Verify firewall settings allow connections on the specified ports. This ensures Kafdrop can retrieve topic and message data.
Setting Up Security Protocols
For secure Kafka clusters, configure Kafdrop with SSL or SASL:
- Add –kafka.security.protocol=SSL for SSL connections.
- Use –kafka.sasl.mechanism=PLAIN for SASL authentication.
- Provide credentials via –kafka.sasl.jaas.config.
- Store sensitive data in environment variables for safety. Test the connection to ensure authentication works without exposing credentials.
Customizing Kafdrop Settings
Kafdrop allows customization through command-line arguments or a properties file. Adjust settings like UI port (–server.port=9001), message inspection depth, or refresh intervals. For Docker, set environment variables in docker-compose.yml. In production, configure logging levels to capture detailed diagnostics. Regularly review settings to optimize performance based on your cluster’s workload and monitoring needs.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Resolving Connection Errors
Connection issues often arise from incorrect broker or ZooKeeper addresses. Verify the –kafka.brokerConnect parameter matches your Kafka setup. Check network connectivity using telnet <broker> 9092. Ensure Kafka brokers are running and accessible. Review Kafdrop logs for specific error messages, such as “Connection refused” or “Timeout,” and adjust firewall or network settings accordingly.
Handling Dependency Conflicts
Dependency conflicts may occur when building from source or using JAR files. Ensure your Java and Maven versions are compatible with Kafdrop’s requirements. Check the pom.xml file for conflicting library versions. Use mvn dependency:tree to identify and resolve conflicts. Rebuild the project after updating dependencies to ensure a clean installation.
Debugging UI Access Issues
If the Kafdrop UI isn’t accessible at http://localhost:9000, check the port configuration. Ensure the port isn’t blocked by a firewall or used by another application. Verify the Kafdrop process is running with ps aux | grep kafdrop. Review logs for startup errors. For Docker, confirm the container is active with docker ps and inspect logs using docker logs <container>.
Why Choose Kafdrop for Kafka Monitoring?
Kafdrop stands out as a lightweight, open-source solution for Kafka monitoring, offering an intuitive interface and robust features. By following this guide, you can install Kafdrop using Docker, JAR files, or source code, depending on your environment. Properly configuring connections, security, and settings ensures seamless integration with your Kafka cluster. With careful setup and troubleshooting, Kafdrop becomes a powerful tool for managing and monitoring your data pipelines effectively.
Conclusion
Kafdrop empowers seamless Kafka cluster management with its intuitive web interface. This guide detailed installing Kafdrop via Docker, JAR files, or source code, ensuring flexibility for any environment. Proper configuration and troubleshooting enhance its effectiveness for monitoring topics and consumer groups. By implementing these steps, you’ll streamline Kafka operations, boost productivity, and maintain robust data pipelines. Leverage Kafdrop’s capabilities to simplify cluster oversight and drive efficient, reliable performance.